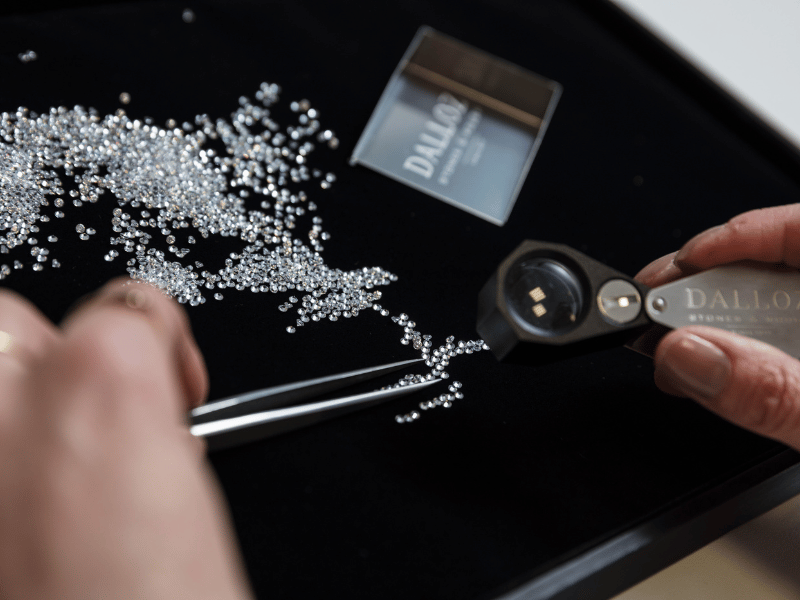
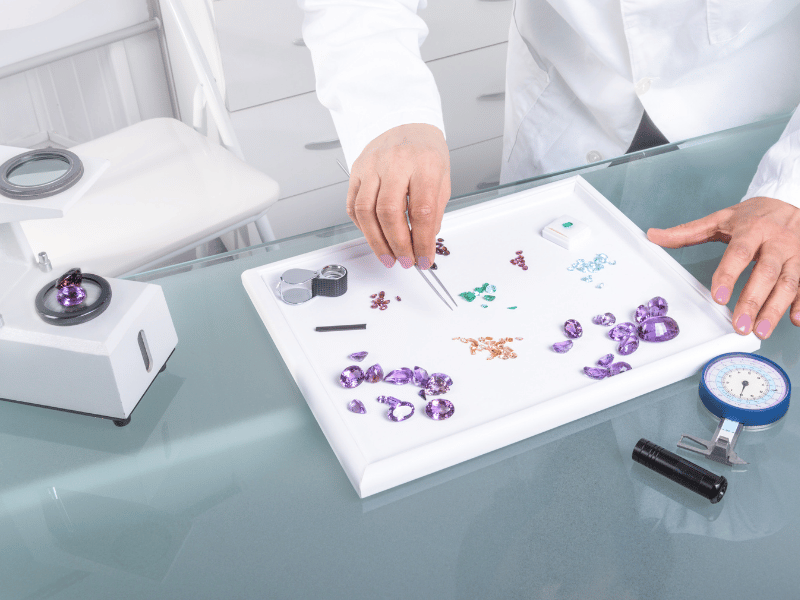
Since the 18th century, many stone cutting factories have been establisSince the 18th century, the cutting of synthetic or natural stones has been an integral part of the Jura region’s heritage. Numerous cutting workshops were established there, making it one of the birthplaces of the lapidary trade in France. In 1917, the Dalloz company was founded to preserve this legacy, threatened by war. Thus began our story, rooted in the demanding art of stone cutting…hed in the Jura region. It is one of the French cradles of the lapidary professions. In 1917, Dalloz was created in order to preserve this heritage, threatened by the war. It is thus with the lapidary that our history began…
What is the lapidary industry?
The lapidary industry includes all the processes used to shape a stone (most often natural and synthetic gems). The goal is to enhance each gem value by playing with shape, the number of facets and angles of the facets.
The cut determines the quality of stones as well as its color. An ideal cut maximizes the brilliance of a gem, giving it the best possible shine.
Stone cutting is the skill of the lapidary; an exceptional profession requiring great know-how.
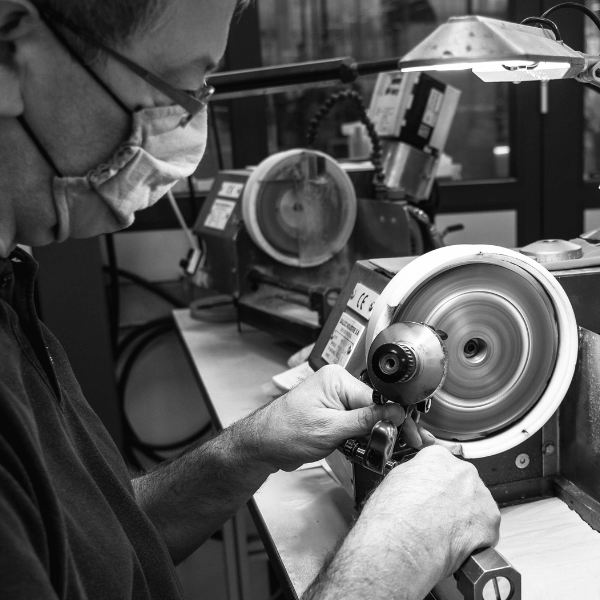

What are the ways to cut?
The cutting process is done in 4 main steps.
- Once the rough is extracted for fine stones, or created for synthetic stones, it is cut into several pieces: this is the sawing. It is used to eliminate the defects of constitution (inclusions, impurities …).
Depending on their crystallization, some gems such as diamond and topaz are cleaved. The cleavage aims to cut the stone along its axes of crystallization in order to obtain two distinct parts, like sawing. - The stone is then cut, gradually revealing the desired final shape. Diamond saws or other chipping machines are used to achieve this result.
- The third step is to give the gem its final shape. The lapidary performs symmetry work to make facets appear (faceting) or give the stone a cabochon shape or other.
- Finally, the gem is polished, thus reinforcing its brilliance.
These steps can be done either manually or with the help of automated machines.
Manual or machine cutting?
This choice can be guided by rough prices, the quantity of gems to be cut, or customer requirements in terms of cutting precision. The cutting of synthetic or natural stones also relies on the lapidary’s expertise, which includes a refined analysis of the material to determine the most suitable cutting process. Depending on the characteristics of the rough (friability, inclusions, impurities), the lapidary may favor hand cutting.
Generally speaking, machine cutting is used in major lapidary industries, whereas hand cutting is preferred in craft industry.
Hand cutting
Hand carving is the traditional method of stone cutting, requiring the skill of the lapidary.
Manual faceting machines are more or less elaborate. The simplest are polishing discs used to shape the stone “by eye”, giving it right angles. The more complex ones allow angles for facets to be displayed and can have symmetry marks, allowing greater precision when cutting.
Automated cutting
Over the years, technologies have improved to offer automated systems capable of replacing human work in the cutting of synthetic or natural stones. The cutting stations can be automated by means of programs defining the actions to be performed on the material—such as sawing, polishing, or other gemstone cutting processes. In this category, the cutting can be mechanical, but also performed using LASER or high-pressure water jet systems. In addition, mechanical arms can be used to move the stones between the different cutting stations.
Automated cutting is fast, ideal for mass production, and ensures good stone calibration, making it particularly useful in modern lapidary craft. However, despite the precision cutting capabilities of machines, human verification remains essential to detect design flaws or material defects. This is where quality control plays a critical role.
Once the work of the lapidary or automated machines has been completed, the final stones are sent to the jewelry workshops, ready to be set on jewelry or to be used as ornaments of any kind.

